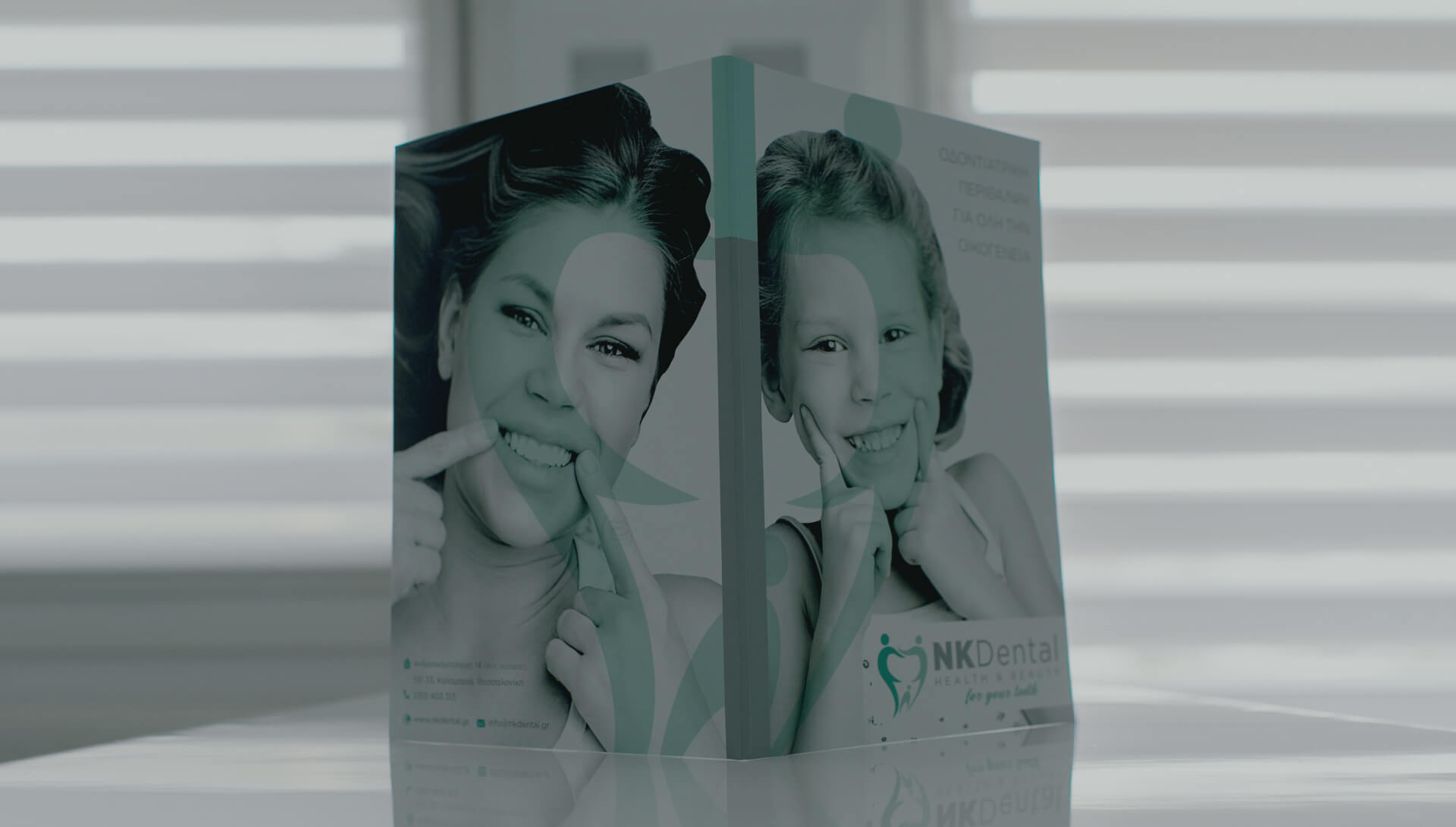

PEDIATRIC DENTISTRY
We take care of our little patients…. We eliminate fear of the dentist!
The first visit to the dentist - pediatric dentist
The first visit to the dentist - pediatric dentist should be conducted within the very first months of the infant’s life. The visit usually takes place when the first baby tooth erupts or within 6 months after eruption. The purpose of the first visit is to inform parents about oral hygiene, the development of the oral system at early ages, and dietary habits that promote dental health. Primary aim of the first visit of the child to the dentist is to get familiar with the dental office and the procedure of dental examination.
Caries on primary teeth – tooth decay
The disease with the highest prevalence among children worldwide is tooth caries. Caries can appear in young patients from a very early age, even a few months after the eruption of baby teeth. It is caused by bacteria, which produce acids and lead to decalcification of the teeth. Cariogenic bacteria are fed from carbohydrates and sugar and the product of their metabolism are acids. The acids destroy enamel and dentin and thus cavities are created. Parents and caregivers can carry over these cariogenic bacteria to children up to the age of 18 months. For that reason, parents and caregivers need to take care of their own oral health. Preventing caries is especially important from the eruption of the first baby tooth. Proper oral hygiene and frequent brushing help teeth withstand acid attacks. Depending on the age of the child, brushing can be done by himself or with the help of a parent. The use of toothpastes that contain fluoride helps to develop a protective shield against caries. At the same time, an important preventive factor is to avoid foods that contribute to the development of caries, such as sweets, juices containing sugar etc.
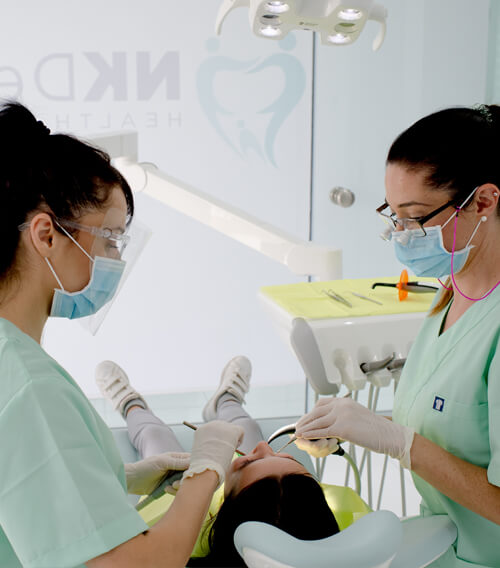
- Filling: Fillings on primary teeth restore missing dental tissues and stop the development of caries towards the tooth’s nerve.
- Pulpotomy: It is a type of endodontic treatment for children, which is applied mainly to primary molars and is a quite quick and painless procedure.
- Dental crowns (caps) for baby teeth: In case of extensive tooth decay, dental caps are being placed on primary teeth to restore missing dental tissues. The dental crown will fall out along with the baby tooth and does not impact the eruption of permanent teeth.
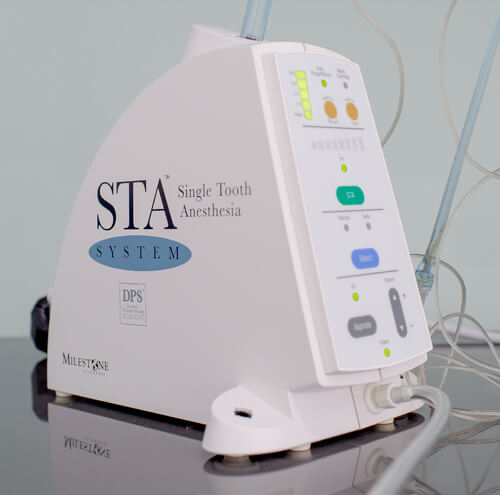
Pediatric anesthesia at the dentist - STA The Wand
Pediatric anesthesia at the pediatric dentist is necessary in order to complete, painlessly and effectively, a treatment on baby teeth. In young children, the process of “giving an injection" is difficult psychologically. At the dental clinic NK Dental in Kalamaria, we use special equipment - The Wand -, to anesthetize the corresponding mouth region. This technique involves the mechanical injection of the anesthetic liquid in a slow and controlled way, while the extent of anesthesia is limited to the respective tooth that needs treatment. In this way, the discomfort that young patients feel is minimized and a basis for good cooperation and trust with the pediatric dentist is created. Children do not experience anxiety and fear of the dentist, and from the moment the tooth "falls asleep", it becomes possible to complete the treatment easily and quickly.
Dental trauma
Dental trauma or accident involving teeth, refers to injury of one or more of a child's baby or permanent teeth. Such traumata occur quite often in children who are actively involved in sports, as well as in adolescents. More than 25% of the patients have experienced a tooth injury between the ages of 6 and 18. A dental accident, such as tooth fracture / injury of lips and gums / concussion / luxation / increased mobility / extrusion / intrusion / avulsion (the tooth falling out of the mouth with its complete root), may occur at any time. Depending on the type of dental injury, the treatment strategy varies. The most important thing, however, is to turn up immediately at the dentist's office when an accident occurs! Early treatment is the most decisive factor for success and effectiveness of the applied therapy
Fluoridation of children’s teeth
Fluoridation of teeth is the most appropriate and effective treatment to prevent tooth decay and increase the long-term survival of dental tissues. The local application of fluoride contributes to recalcification of enamel and inhibits the development of caries. At the same time, it offers an antimicrobial effect.
Bad oral habits (pacifier overuse, baby bottle overuse, thumb-sucking, lip-biting/sucking)
Many children tend to "suck" their fingers or make excessive use of the pacifier in the first years of life. It is advisable to break off such oral habits at the very latest between the 2nd and 3rd year of life. If such habits persist at elder ages, there may be a negative effect on the development of the jaw / bone, on the occlusion of teeth (crooked), on the type of swallowing and on speech function. The pediatric dentist can inform the parents about the possible dangers and help the little patient with aborting such habits.

Dental phobia / Patients with disabilities/ Dental treatment in general anesthesia (St. Luke’s Hospital S.A.)
- Dental phobia
- How do we treat
dental phobia? - Dental care for disabled patients
- Dental treatment in general anesthesia
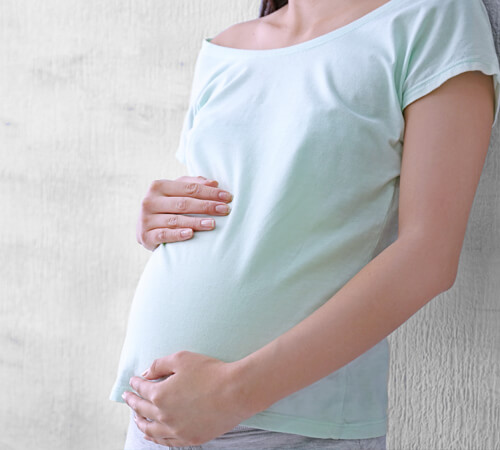
Pregnancy
The formation of primary, as well as of some of the permanent teeth in the jaw, begins already during pregnancy. The mother's diet or medication she takes, may affect the development and health of baby teeth. At the same time, hormonal changes occuring during pregnancy may affect the mother’s gingival tissues and cause frequent bleeding during brushing (pregnancy gingivitis). For these reasons, it is important to inform pregnant women about oral hygiene issues concerning themselves and their babies.

Molar-incisor hypomineralization (MIH)
Molar Incisor Hypomineralization (MIH), is a developmental condition whose etiology has not been clarified yet. It usually appears on one to four first permanent molars and on the front teeth. Hypomineralised teeth are more susceptible to caries and wear compared to normal teeth. White, yellow or brown spots appear on them at eruption. In addition to the aesthetic disadvantage, these teeth show severe sensitivity while brushing, chewing, speaking, etc. Children with MIH need more intensive dental care and should be put in a strict recall program. Early diagnosis is essential to prevent further destruction of dental tissues. The diagnosis can be set by the pediatric dentist even if the tooth has not fully erupted yet. In these cases, fluoridation may reinforce enamel against decay until the tooth fully erupts.
